
Scientific Injection Molding
To have confidence in your manufacturing quality, you want to make sure your contract manufacturer has the right philosophy about quality. This means looking at the lead indicators of quality rather than the lag indicators. Unfortunately, many contract manufacturers still use lag indicators which work against their quality aim.
Injection molding quality processes share many similarities with the general healthcare industry. Both injection molding and healthcare monitor the same vital signs as quality indicators: temperature, speed, and pressure. Both injection molding and healthcare employ nominal targets for each indicator, and both account for variation. Comparing quality processes in injection molding with healthcare helps develop a deeper understanding of mold qualifications and, specifically, Scientific Molding.
Injection Molding Vital Signs
Over the centuries, the medical community has come to focus on four vital signs to monitor patient status: body temperature, speed both for heart rate and for respiration rate, and blood pressure. A change in any of these outside of safe ranges alerts healthcare providers to potential problems. Vital signs do not always indicate whether something is wrong or what is wrong. They do serve as a red flag to investigate further.
The same holds true for injection molding, starting with mold qualification. The Process Engineer uses Scientific Molding to establish the injection molding parameters that will produce quality parts. Scientific Molding looks at the injection molding temperature, speed, and pressure. You can learn more about the Scientific Molding Process and read our previous case studies on Design of Experiments and Scientific Processing.
Injection Molding Process Tolerances
Variation is a fact of life. Healthcare acknowledges variation in vitals. For example, children have different target vitals from adults, and vital signs vary from moment to moment during different activity levels. Slight deviations from the target do not raise the same alarms as greater deviations. In injection molding, we typically think of tolerances as applying to dimensions. However, tolerances apply to processes because variation exists everywhere.
Every injection molding process experiences variation so every injection molded product varies on some level. If Process Engineers establish only the target injection molding process, when their process varies (and it will), their level of confidence in the quality of their process suffers.
Process Engineers establish the full injection molding process window using Scientific Molding. Knowing that the Upper and Lower Control Limits fall within the Specification Limits gives the Processing Engineer a high degree of confidence that the injection molding process will produce quality parts.
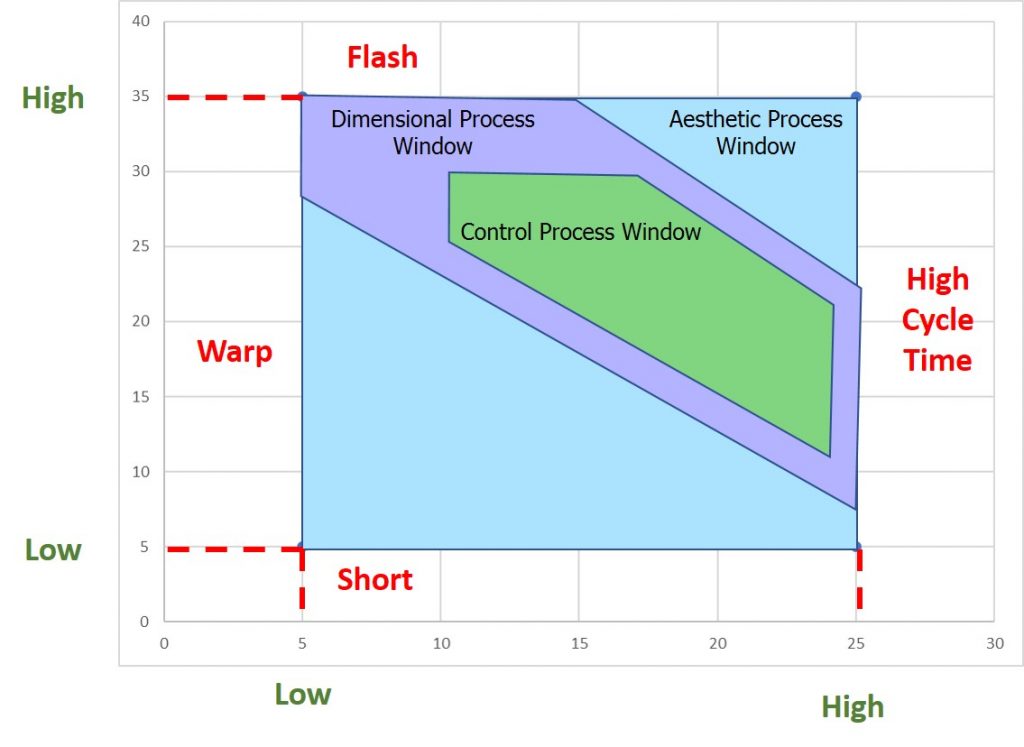
During mold qualification, they intentionally push the processing boundaries to see how far they can go and still produce quality parts. They create three injection molding process windows. First, they determine the Aesthetic Process Window, which achieves aesthetic quality. Within that, they find the Dimensional Process Window, which achieves dimensional quality. Within that window they then establish the Control Process Window, which achieves statistical capability.
Injection Molding Process Monitoring
The world of healthcare has started paying attention to preventive measures such as mindful eating, exercising, and avoiding injury instead of dealing with issues after the fact. These inputs serve as lead indicators of health while body temperature, heart rate, respiration rate, and blood pressure serve as lag indicators.
By contrast, for injection molding, temperature, speed, and pressure serve as lead indicators. Inspecting parts looks at lag indicators. In other words, monitoring aesthetics or part dimensions looks at what has already happened. Scientific Molding allows processors to monitor the lead indicators of injection molding. Temperature, speed, and pressure serve as the lead indicators of injection molding quality after locking and transferring the part design.
The Processing Engineer programs these processing parameters along with the processing tolerances into the injection molding press. If, for some reason, the injection molding process parameters exceed the allowable processing window on a given shot, the machine knows to drop the parts in the reject bin instead of on the conveyor. The parts might conform to aesthetic and dimensional requirements. But rather than attempting to inspect quality into the parts, we want to inspect the process and have confidence that we produce quality parts.
In injection molding we want quality parts, so we establish a quality process at the beginning through Scientific Molding. When we transfer the design to manufacturing, we monitor the injection molding process window. If our injection molding vitals remain within their processing tolerances, we can say with a high level of confidence that we are using a quality process that produces quality parts.
To speak to a Natech Engineer about your program call us at (631) 580-3506 or email us at info@natechplastics.com.